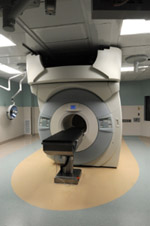
 Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (ioMRI) uses powerful scans to help neurosurgeons image the patient's brain during surgery, or intraoperatively, to help determine if all of the tumor or lesion has been removed during tumor or epilepsy surgery. For some kinds of tumors, it is difficult to distinguish the tumor from normal brain tissue just by looking at it. This type of scanning during surgery helps the surgeon be more accurate in the initial operation, and, through selected cases, we have demonstrated a reduction in the need for reoperations when using ioMRI.
Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging (ioMRI) uses powerful scans to help neurosurgeons image the patient's brain during surgery, or intraoperatively, to help determine if all of the tumor or lesion has been removed during tumor or epilepsy surgery. For some kinds of tumors, it is difficult to distinguish the tumor from normal brain tissue just by looking at it. This type of scanning during surgery helps the surgeon be more accurate in the initial operation, and, through selected cases, we have demonstrated a reduction in the need for reoperations when using ioMRI.