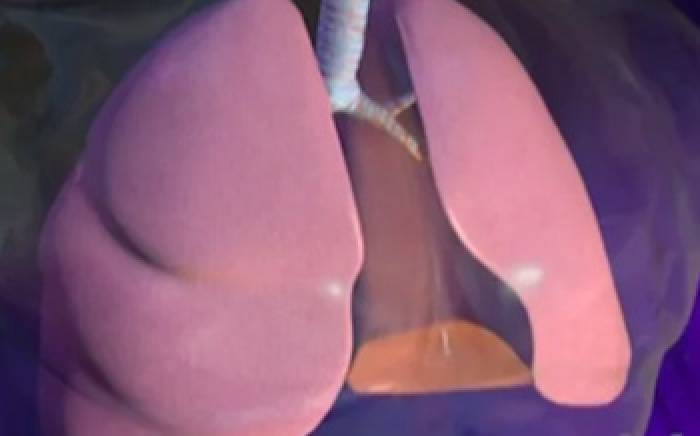
During normal respiration, air travels through the nose, down the trachea, and into smaller and smaller airways called bronchi. In some cases the smooth muscle that wraps around the bronchi may constrict and mucus levels can increase. This makes breathing difficult.
Generally this condition is treated with medication called bronchodilators. The most common types of bronchodilators are anticholinergics and beta-2 agonists. These drugs are inhaled, travel down the airway and bind to bronchial smooth muscle cells. This results in muscle relaxation and decreased levels of mucus, which allows for easier breathing.