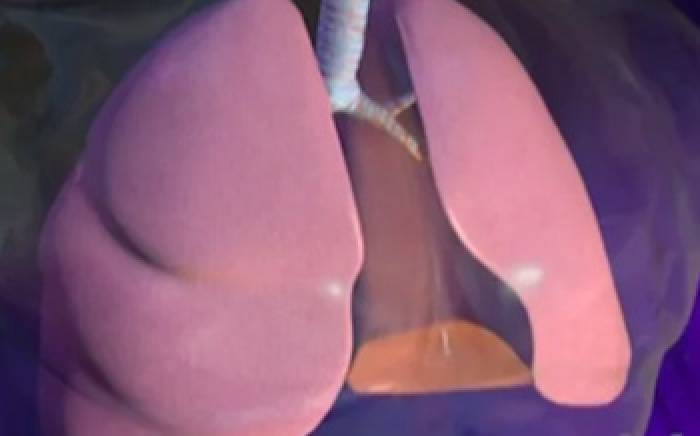
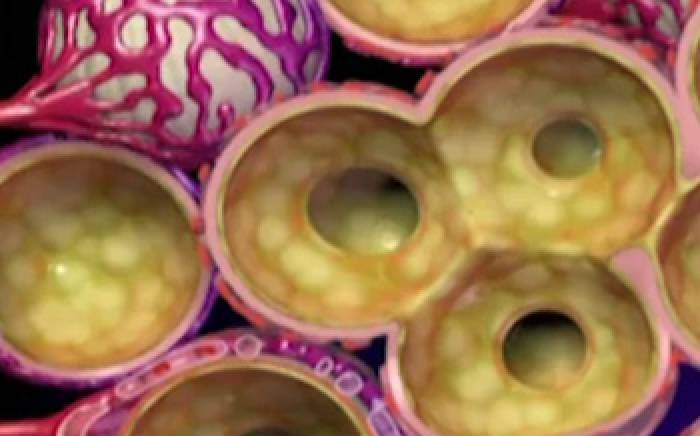
During normal respiration, air travels through the nose, down the trachea, and into smaller and smaller airways called bronchi. The bronchi divide into bronchioles and finally into tiny grape-like clusters of thin, fragile sacs called alveoli.
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, or bronchi. When the cells of the bronchial-lining tissue are irritated beyond a certain point, the tiny hair cells (cilia) which normally trap and eliminate pollutants, stop functioning. In response, a heavy secretion of mucus develops, which causes the characteristic cough of bronchitis. The inflammation may be caused by viruses, bacteria, smoking or inhalation of chemical pollutants or dust.